Filters
Filters define the report criteria, setting the boundary conditions for the data displayed by your report. With Reporting advanced filter conditions you can set multiple logical conditions to further refine what data will appear in both your Summary and Detail reports.
Reporting filters are shared between the summary and detail reports of the same name so that report results from both share the same filter conditions.
General Operation
Open the Filters editor with a click on Edit Filters or click any existing filter condition and the Filters panel branching editor will expand as is shown below.
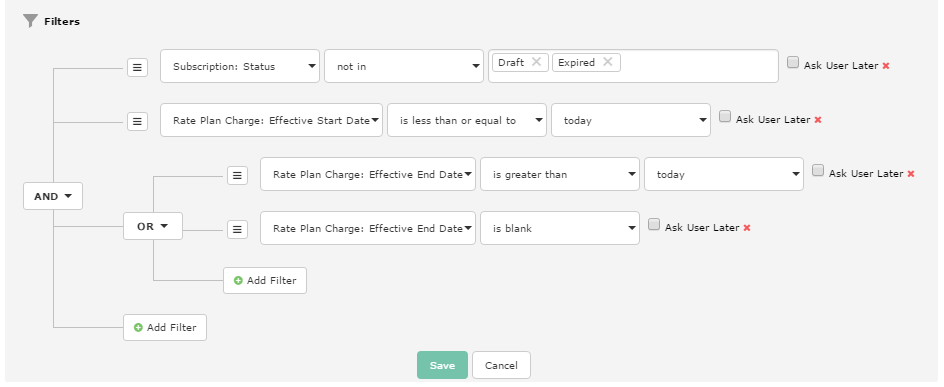
- Filters with AND conditions restrict report results to data that matches all AND criteria.
- Filters with OR conditions open report results to include data that matches any OR criteria.
Toggle between AND and OR by clicking the branch.
- Each filter branch can include nested filter criteria to further refine the condition as necessary.
Create new branches with a click on: 
Click Add Filter to create more filters on a new or existing branch.
Remove filters with a click on the small red X displayed at the end of the line.
Click Cancel if you want to revert all changes to the last saved filter.
Click Save to apply the filter and to refresh the report preview.
Defining Filters
|
1. Select the data source object |
When you add a filter the first field displays all the data source objects available in the data source you selected to create the report. Narrow the displayed list by typing just a few characters to show only those data source objects with that string. |
|
2. Set an operator |
The data type of the selected data source object determines what logical comparisons can be made. See below for information about Reporting operators. |
|
3. Set a filter value |
Filter values can be static, relative, or entered at run time. See below for details. If you want to use a backslash ( |
|
4. Save |
Save the filter changes to see a preview of the results or save and run the report. If you save just the filter changes to preview the report results, make sure to Save Report & Run or Save the report if you want the changes to be permanent. |
Filter Values
Filter values may be defined three different ways:
A) defined ahead of time - at design time,
B) defined relative to the day (and time) that the report is run, or
C) specified at the time the report is run (Ask User Later)
A) Setting static comparison values
Set a specific value for any filter and data that meets the criteria will be shown.
To set a specific date or date range that remains static for your report, select "the specific date" or "the specific date range" and specify the date using the calendar date picker or by manual entry according to. Hour, minute, and seconds for date-time data types can be modified by manual typed entry according to the example schema in the interface.
B) Setting relative date comparison values
Many report definitions are better when the results reflect a date that is relative to the date when the report is run. There are several different options in Zuora for doing this.
- a certain amount of time in the past
- yesterday
- today
- tomorrow
- a certain amount of time in the future
- the previous (evaluates full periods of time in the past: day(s), week(s), month(s), quarter(s), year(s), or accounting period(s) not including partial periods of time - available when operator is during or is not during)
- the current (evaluated from run time including this day, week, month, quarter, year, or accounting period even if that period is incomplete - available when operator is during or is not during)
- the next (evaluates full periods of time in the future: day(s), week(s), month(s), quarter(s), year(s), or accounting period(s) not including partial periods of time - available when operator is during or is not during)
C) Ask User Later - Create filters that prompt the user to enter the value at runtime (previously known as "parameterized filters")
When a report is run that has a filter with "Ask User Later" checked, the user running the report is prompted to enter a filter value for that run. The filter and the value you predefine is shown and can be used as the default report run condition. The filter default value is also used when the report is scheduled to run.
Being able to change filter values at runtime offers flexibility. Additionally when some users only have permission to run and view reports, those users can't change report definitions, but they can change filter values to frame report results according to their focus.
Check the Ask User Later box on a filter to enable a runtime prompt to change the filter value. You must still pre-define the filter with the data source object and operator, and set the default filter value.
Different types of filters can be set according to the needs of your report:
- Filters can be based on static values and conditions.
- Filters on date-time data types can be defined relative to whatever day that report is run in the future.
- Set filters to ask the user later for the values at the time of the report run.
Use the Operators section below as a reference if needed to complete your filter.
Operator reference
The data type of the object selected determines what logical operators may be used.
For numeric data types the following operators are available:
- is equal to (=)
- is not equal to (≠)
- is greater than (>)
- is less than (<)
- is greater than or equal to (≥)
- is less than or equal to (≤)
- in (specify a set of values; only an exact match to one of the values will pass the filter)
Each value should be separated by a comma. - not in (specify a set of values; only an exact match to one of the specified values will filter out the data point)
Each value should be separated by a comma. - is blank (null values are blank, zero is not blank)
- is not blank (null values are blank, zero is not blank)
For date and date-time data types a different set of operators provide conditions to filter time:
- is not equal to (≠)
- is greater than (after a specified date or date-time - not inclusive of the specified point)
- is less than (before a specified date or date-time - not inclusive of the specified point)
- is greater than or equal to (after a specified date or date-time - includes the specified point)
- is less than or equal to (before a specified date or date-time - includes the specified point)
- is during (two dates define the window in which data values pass the filter - date endpoints are included)
- is not during (two dates define a window in which data values are filtered out of the display set - values that equal the endpoints will be excluded)
- is blank
- is not blank
Date and date-time data types require that you to set a point in time that can be absolute or relative based on some arbitrary day in the future when the report is run. Your report filter conditions can compare against the following selections.
- the specific date
- a certain amount of time in the past
- yesterday
- today
- tomorrow
- a certain amount of time in the future
What's Next
Once you have set a filter on your report click Save Report & Run to see the results or just click Save. Reports can be saved to private or shared folders. Refer to the description of Folders and Sharing for more information.
